
Discover Saudi Arabia
Sights
Map
Info
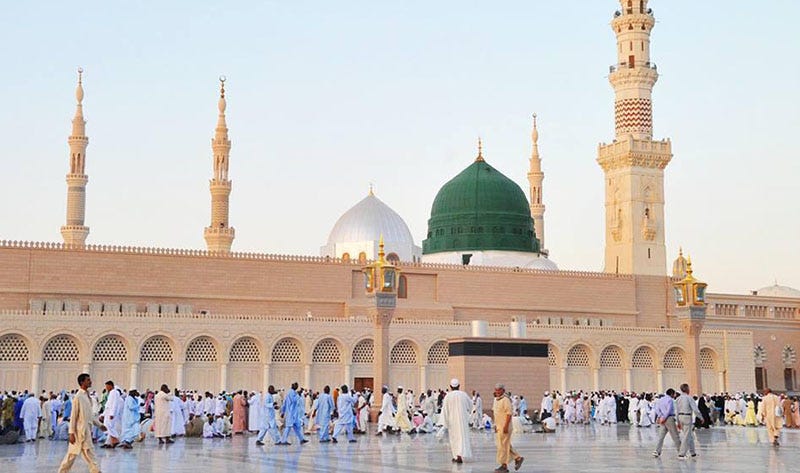
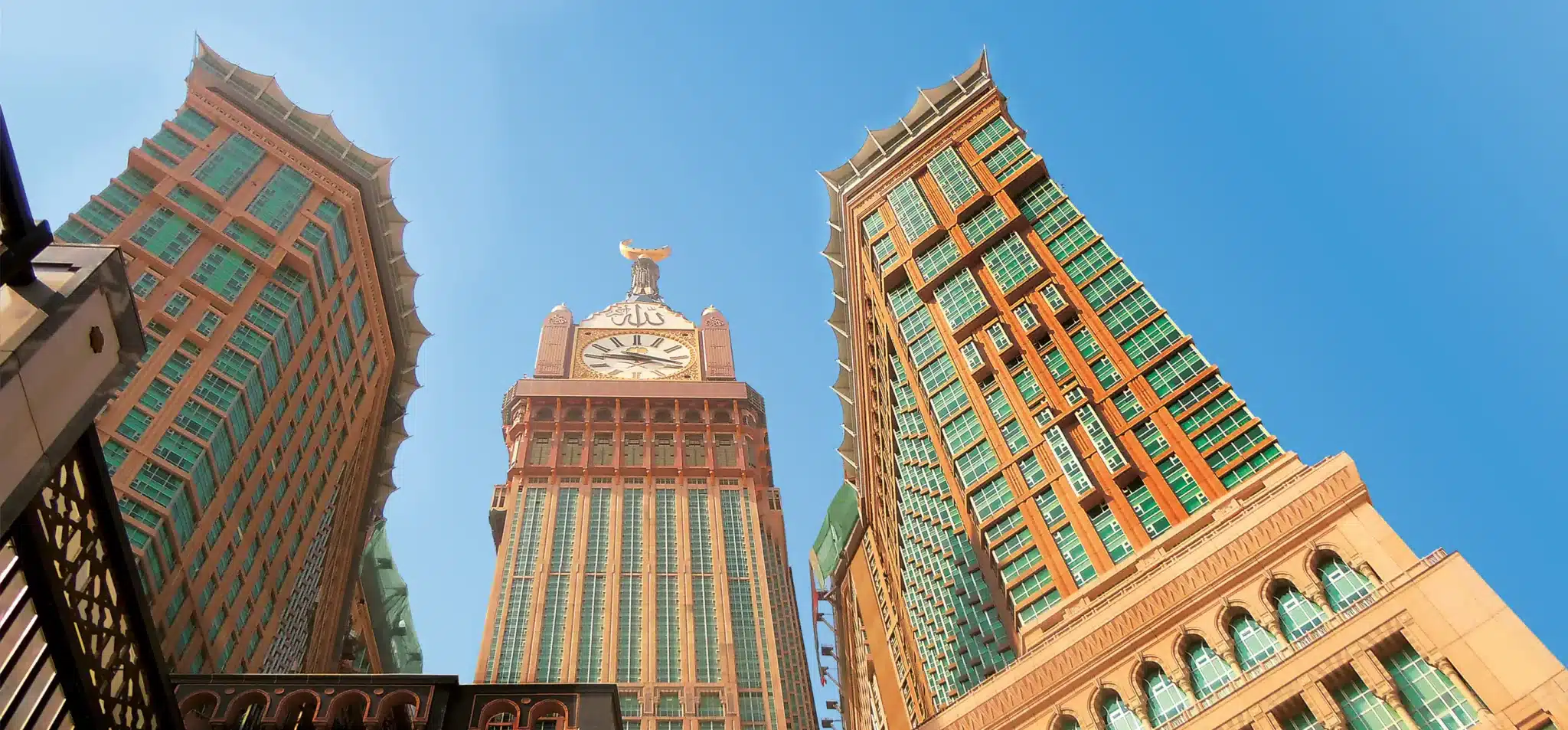
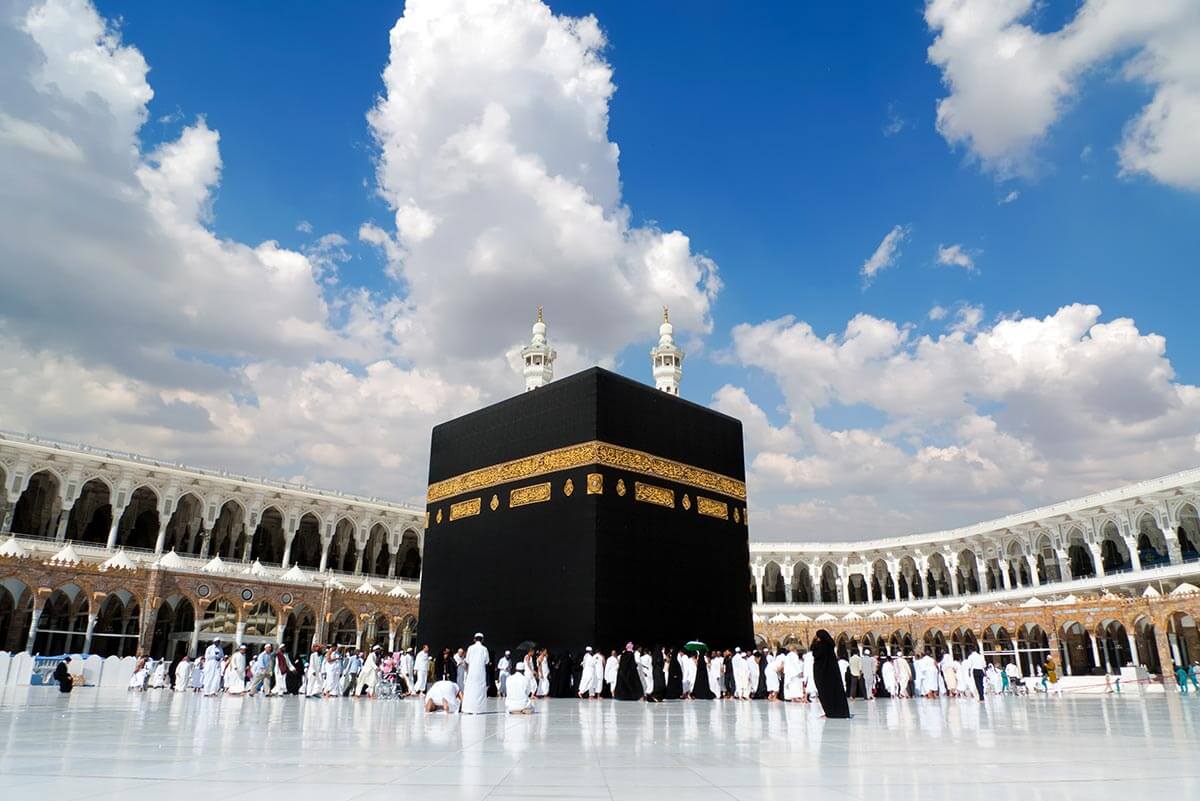
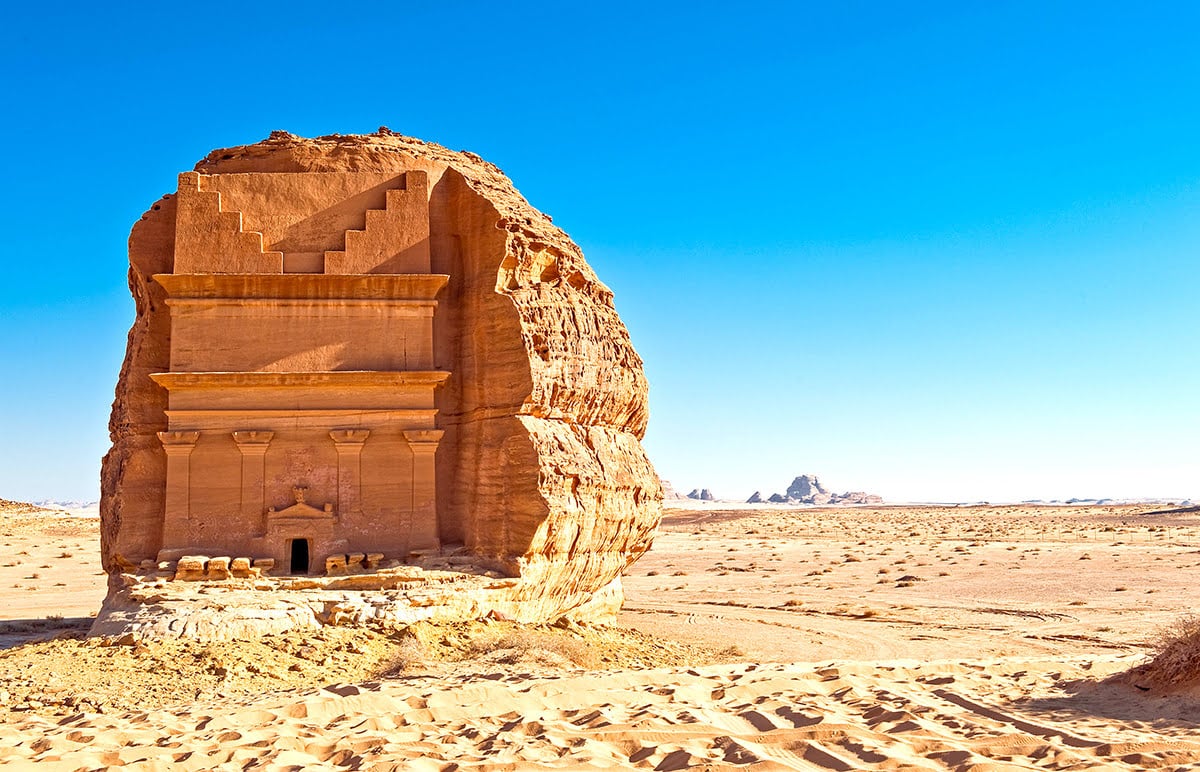
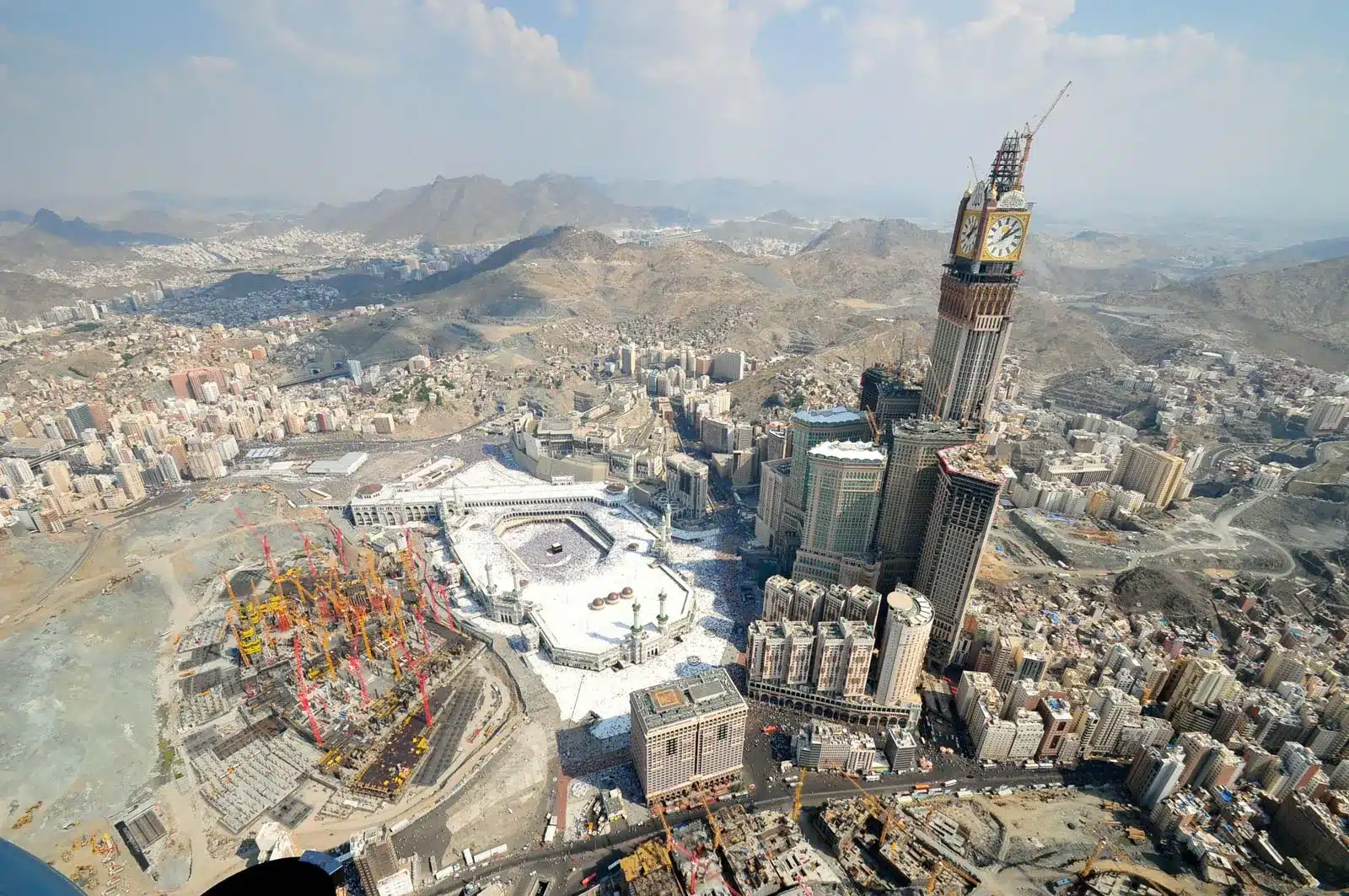
Saudi Arabia, known for its vast deserts, rich cultural heritage, and pivotal role in the Islamic world, is a country that blends deep-rooted traditions with rapid modernization. As the birthplace of Islam, it attracts millions of pilgrims to its holy cities, Mecca and Medina, each year. Beyond its religious significance, Saudi Arabia is home to modern cities like Riyadh and Jeddah, ancient archaeological sites, and stunning natural landscapes. With the kingdom’s Vision 2030 initiative, the country is opening up more to international tourism, making it an intriguing destination for travelers. To ensure a smooth visit, it’s important to understand the visa requirements, transportation options, and cultural norms in Saudi Arabia.
Visa and Passport Requirements
Visa Requirement: Saudi Arabia now offers e-Visas for tourists from many countries, allowing for short stays. Pilgrims traveling for Hajj or Umrah must obtain a special visa.
Passport Validity: Your passport should be valid for at least six months beyond your planned entry date.
Entry Restrictions: Certain items are prohibited from entering Saudi Arabia, such as alcohol and religious books other than the Quran.
Transportation
Public Transport: Public transportation is developing rapidly, with buses available in major cities and a growing metro system in Riyadh.
Taxis and Ride-Sharing: Taxis are widely available, and ride-sharing services like Uber and Careem are popular, offering safe and reliable transportation.
Car Rentals: Renting a car is a convenient option for exploring the country, but be aware that traffic laws are strictly enforced.
Accommodation
Hotels: Saudi Arabia offers a range of hotels, from luxury chains to more affordable options, particularly in major cities and religious sites.
Resorts and Villas: For those looking for a more private experience, resorts and rental villas are available, particularly along the Red Sea coast.
Pilgrim Accommodation: During Hajj and Umrah, special accommodations are available to cater to the large influx of pilgrims.
Dining
Saudi Cuisine: Traditional dishes such as kabsa (spiced rice with meat), mutabbaq (stuffed pastry), and dates are central to Saudi dining, reflecting the country’s rich culinary heritage.
Dining Customs: Restaurants typically offer separate sections for families and singles; it is important to observe these divisions when dining out.
International Cuisine: In major cities like Riyadh and Jeddah, you’ll find a wide variety of international restaurants, from fast food to fine dining.
Cultural Considerations
Dress Code: Modest dress is required, with women expected to wear an abaya in public; men should avoid wearing shorts and sleeveless shirts.
Public Behavior: Public displays of affection are frowned upon, and it’s important to respect local customs, particularly during prayer times.
Social Etiquette: Saudis are known for their hospitality; it is customary to accept invitations to homes or social gatherings and bring a small gift as a token of appreciation.
Language
Language: Arabic is the official language, but English is widely spoken in business and tourist areas, especially in major cities.
Signage: Most public signs and information in urban areas are available in both Arabic and English, easing navigation for non-Arabic speakers.
Learning Basic Phrases: Knowing a few Arabic phrases, such as “Shukran” (Thank you) and “As-salamu alaykum” (Peace be upon you), can be helpful and appreciated by locals.
Technology and Communication
Mobile Connectivity: Saudi Arabia has excellent mobile network coverage, and purchasing a local SIM card is easy and convenient for data and calls.
Wi-Fi Access: Free Wi-Fi is widely available in hotels, cafes, and public spaces, though speeds may vary, particularly in remote areas.
Internet Censorship: Some websites and VoIP services (like Skype) may be restricted, so it’s advisable to use a VPN for unrestricted access.
Shopping and Payment
Credit Cards: Credit cards are widely accepted in Saudi Arabia, particularly in cities and tourist areas, but it’s advisable to carry some cash for smaller purchases or in rural areas.
Currency Exchange: The Saudi Riyal (SAR) is the official currency, and currency exchange services are available at airports, banks, and exchange bureaus.
Shopping Etiquette: Bargaining is common in traditional markets (souks), while prices in malls and stores are generally fixed.



















